Introduction
Imagine a scenario where the ground opens up, and everything we know about dental implantology is transformed. We enter a new dimension where bone limitations are no longer insurmountable barriers. Welcome to the world of zygomatic implants. If you’ve ever doubted dentistry’s ability to reinvent itself, you’re in for a surprise. The story of zygomatic implants is a tale of innovation, daring and transformation that promises to change the lives of those facing serious bone challenges forever.
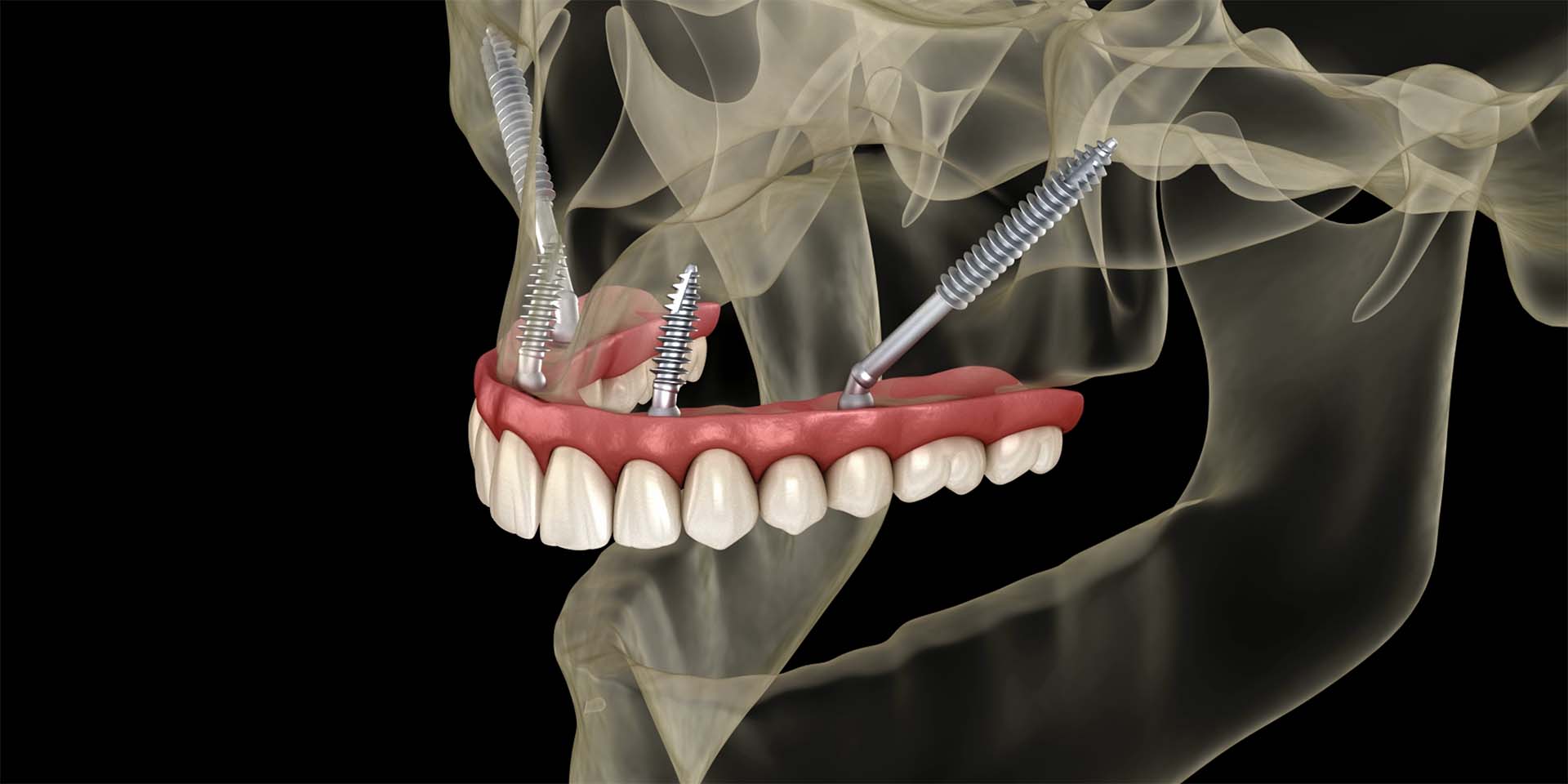
Zygomatic Implants: An Innovative Alternative
Zygomatic implants have emerged as a revolutionary solution for patients who have suffered severe bone loss in the jaw. First developed by Professor Branemark in the 1980s, these implants are longer than traditional implants and are anchored in the zygomatic bone, or cheekbone, offering a viable alternative for those who cannot receive conventional implants.
Statistics and Facts:
- Incidence of bone loss: Approximately 25 per cent of patients who need dental implants have significant bone loss in the upper jaw.
- Success Rate: Studies indicate that zygomatic implants have a success rate of over 95 per cent over 10 years.
Advanced Procedures and Techniques
The procedure for placing zygomatic implants is complex and requires a high level of specialisation. Unlike traditional implants, which are inserted directly into the jawbone, zygomatic implants are fixed into the zygomatic bone via an oblique route.
Stages of the procedure:
1. Pre-operative planning: Use of CT scans to assess bone structure and plan surgery.
2. Anaesthesia and Preparation: The patient is anaesthetised and the area is prepared for surgery.
3. Implant insertion: The implants are placed through the jawbone into the zygomatic bone.
4 Fixation and stabilisation: After insertion, the implants are fixed and stabilised, ready to support the dental prosthesis.
Advanced Techniques:
- Computer-Assisted Surgical Navigation: Increases the precision of implant placement.
- 3D printing: To create personalised surgical guides and improve results.
Benefits of Zygomatic Implants
The benefits of zygomatic implants are substantial, especially for those who previously had few treatment options.
Advantages:
- Reduced Treatment Time: Eliminates the need for bone grafts, allowing for faster rehabilitation.
- Greater stability: Due to the anchorage in the zygomatic bone, it offers a more solid base for the prosthesis.
- Increased Patient Satisfaction: Significant improvement in masticatory function and facial aesthetics.
Impact on Quality of Life:
Studies show that patients with zygomatic implants experience notable improvements in quality of life, including increased self-esteem and the ability to socialise.
Relevant Studies and Statistics
Research into zygomatic implants has revealed impressive data on their effectiveness and safety.
Important data:
- Implant survival rate: Longitudinal studies show an implant survival rate of 97.86% over 12 years .
- Complications: Although the complication rate is low, sinusitis and peri-implant infections can occur and are managed with appropriate clinical interventions.
- Patient satisfaction: More than 90 per cent of patients report being satisfied or very satisfied with the results of their zygomatic implants.
Post-operative care and maintenance
After zygomatic implants have been placed, post-operative care is crucial to ensure the longevity and success of the treatment.
Recommendations:
- Oral hygiene: Maintain strict oral hygiene to avoid infections.
- Regular appointments: Periodic visits to the dentist to monitor and maintain the implants.
- Diet: Follow a soft diet in the first few weeks after surgery to facilitate healing.
Practical Tips:
- Use interdental brushes and oral irrigators for effective cleaning.
- Avoid harmful habits such as smoking, which can jeopardise the health of the implants.
Conclusion
Zygomatic implants represent a significant advance in dental medicine, providing an innovative solution for patients with severe bone loss. With advanced techniques and a high success rate, these implants offer new hope for those who previously had no viable options. The continuous evolution of techniques and commitment to clinical excellence ensure that more and more people can benefit from these advances. Are you ready to explore the possibilities that zygomatic implants can offer?
Scientific references:
Malevez, C., Hermans, M., Bouhy, A., & Daelemans, P. (2004). Use of zygomatic implants to deal with resorbed posterior maxillae. Periodontology 2000, 33, 82-89.
Chrcanovic, B. R., Abreu, M. H., & Custódio, A. L. (2011). Zygomatic implants for the rehabilitation of the atrophic maxilla: a systematic review. Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 15(4), 261-272.
Davo, R., Pons, O., & Rojas, J. (2010). Immediate function of four zygomatic implants: a 1-year report of a prospective study. European Journal of Oral Implantology, 3(4), 323-334.
Aparicio, C., & Ouazzani, W. (2002). Immediate/early loading of zygomatic implants: clinical experiences after 6 years. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 60(7), 883-889.
Bedrossian, E., Stumpel, L., & Beckely, M. L. (2002). The zygomatic implant: preliminary data on technique and results. International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants, 17(6), 861-865.